Reinforcement Learning
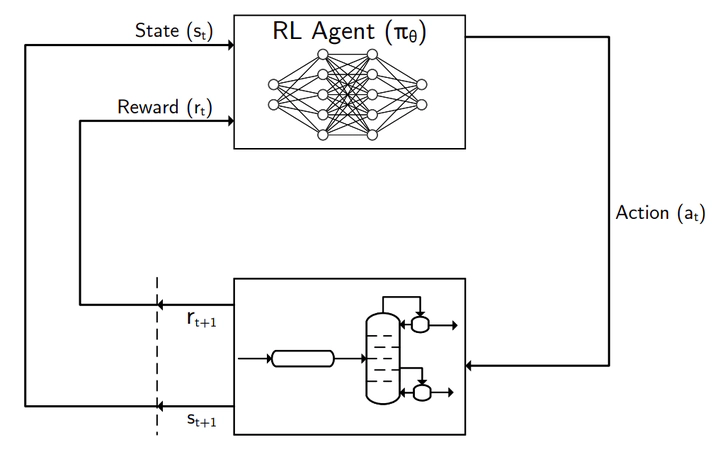
Reinforcement Learning (RL) is a subfield of Artificial Intelligence (AI) which trains Machine Learning models to make optimal decisions. This is done in such a way that the model (or agent; or controller in a process engineering domain) learns how to take optimal actions as it explores the environment in which it resides.
RL has received a lot of attention, notable examples are ``machines" learning to play board games such as Go, or videogames such as DOTA 2 or Starcraft. Furthermore, game-playing is not all that RL is useful for. In previous work we have already optimized chemical processes under this same philosophy.
Reinforcement learning was designed to address the optimisation of stochastic dynamic systems. It so happens that in reality chemical processes are stochastic (due to process disturbances) and in many cases operated in dynamic mode. The difference with traditional RL applied in mainstream AI resides in the fact that RL is “data hungry” and does not consider constraints. This is a major drawback given that processes generally rely on much less data, while unbounded exploration (without constraints) can be dangerous or costly. This project aims to design a new RL algorithm that can be used to optimize complex chemical and biochemical processes which are still unresolved today.